by Ravindra Warang
6 minutes
Nourishing the Future of Pharma: An Introduction to Nutraceuticals
Explore the transformative role of nutraceuticals in enhancing health and preventing diseases.

Many of my friends take dietary supplements daily, weekly or monthly. Quite frankly, my traditional mindset (and a quite little bit of laziness) have resulted in me never understanding or trying nutraceuticals. But, with how popular they’ve become recently, I knew it was time to do some research.
If, like me, you’re not sure what nutraceuticals are. Here’s a detailed guide on supplements and nutraceuticals. Frankly, with how much research I’ve done, this will be the only nutraceuticals guide you need to read! But first, let’s address the important question:
What are Nutraceuticals?
Nutraceuticals are a combination of the words “nutrient, " a nourishing food component, and " pharmaceutical, " a medicine. They are classified into three—namely, dietary supplements, functional foods, and medical foods—according to their natural sources and chemical compositions. They are designed to provide nutrition as well as many health benefits.
Nutraceuticals offer an easy solution to deficiencies, enabling people to supplement their diets with specific nutrients supporting various aspects of their health, from cardiovascular and cognitive functions to digestive health and overall wellness. Still, why exactly are they important in our health and fitness?
Importance of Nutraceuticals in Health and Wellness
Preventive healthcare: Nutraceuticals help in preventing chronic diseases by providing essential nutrients missing from our regular diet.
Increased nutritional value: Modern diets can’t fulfil our current nutritional requirements. Hence, nutraceuticals can be consumed to bridge the gap and provide adequate nutrients.
Target-specific health conditions: Various nutraceuticals are target-specific—They improve the function of a specific part of the human body, e.g., heart health or joint health
Promoting overall wellness: Regular intake of nutraceuticals improves an individual's overall health and wellness, which may result in an increase in their life expectancy.
Easy consumption: Nutraceuticals are convenient and provide many benefits for overall health without significantly changing diet and lifestyle. Don’t worry; we’ll discuss health benefits more in the following sections!
Types of Nutraceuticals
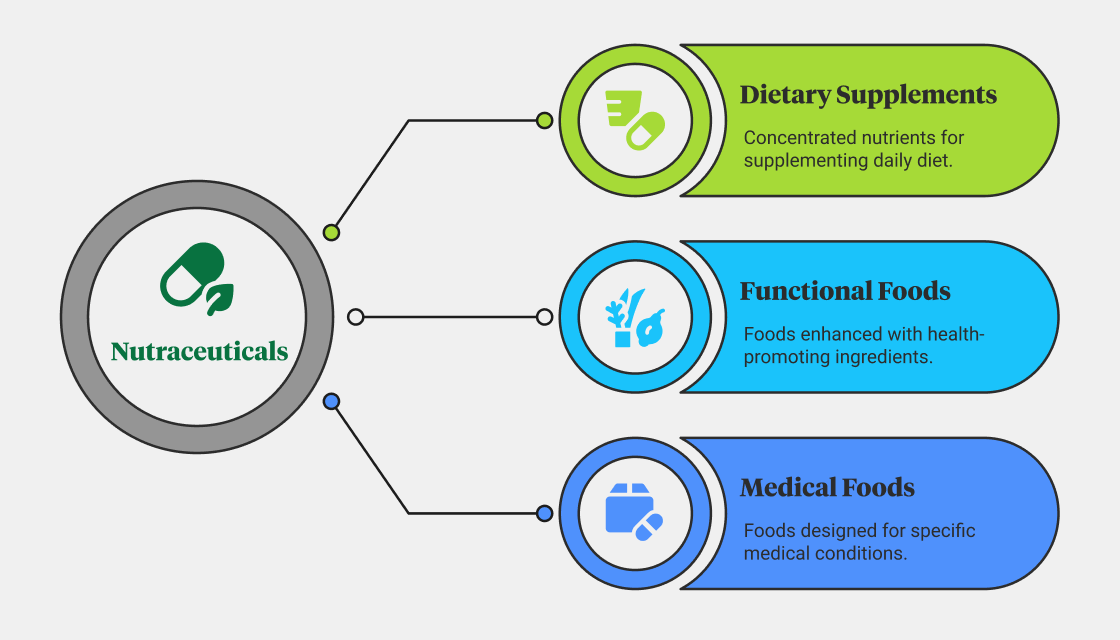
Dietary Supplements
Dietary supplements are the most famous category of nutraceuticals. They are concentrated sources of nutrients (like vitamins, minerals, amino acids, herbs, or other substances) intended to supplement the diet.
They contain nutrients derived from food products and provide nutrition that an individual can’t get from their diet. They also provide nutrients to support specific health goals, e.g., to boost immunity or improve bone health. They are sold as pills, capsules, powders and liquids.
Popular types:
- Vitamins: Essential micronutrients like vitamins C, B and D are essential for the human body to function properly.
- Minerals: Minerals such as calcium, iron, zinc, and magnesium essential for day-to-day activities, are also available. Their availability in insufficient amounts leads to many health problems.
- Herbal supplements: These supplements are derived from different parts of plants (like leaves, oils, roots, fruits, or stems). They have numerous uses; for example, aloe vera is used to treat sunburns.
Functional Foods
Functional foods are whole foods or beverages intentionally modified or enriched with bioactive compounds, essential vitamins, or vital minerals that may reduce the risk of chronic diseases or are necessary for a person's overall health when introduced into a regular diet.
Examples:
- Probiotics: Like yoghurt, probiotics are good for gut health and immunity because they contain live bacteria.
- Fortified foods: Products like fortified cereals or beverages enriched with added vitamins (e.g., vitamin D-fortified milk) to provide sufficient vitamin D.
Omega-3 enriched foods: Eggs or bread containing added omega-3 fatty acids for heart health.
Medical Foods
Medical foods are a distinct category of nutraceuticals formulated to manage specific medical conditions under medical supervision. Anyone can consume dietary supplements and functional foods. By contrast, a prescription is needed for medical foods as they are part of a patient's medical care plan.
How do they help? Medical foods manage conditions such as metabolic disorders (e.g., diabetes, phenylketonuria), gastrointestinal disorders (e.g., Crohn's disease, irritable bowel syndrome), and conditions requiring specialised nutritional support.
Regulations and clinical studies: Clinical studies and trials are being conducted to ensure these are safe and can help improve patient outcomes.
Health Benefits of Nutraceuticals
Nutraceuticals offer many health benefits, which are best understood when categorised by specific health areas. Let’s explore how nutraceuticals support cardiovascular health, cognitive function, digestive health, and overall wellness.

Cognitive Function
It is essential to keep your brain healthy as you age. They help in maintaining brain function and preventing cognitive decline. Their components support brain health and include the following:
- Antioxidants: Vitamin C/E and polyphenols— found in fruits and vegetables—protect brain cells from damage and inflammation, which are linked to cognitive decline.
- Phosphatidylserine: Phosphatidylserine—found in soy and white beans—is essential for maintaining healthy brain cell membranes and is linked to better memory and cognitive performance.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Omega-3s, especially DHA, are the best friend of your heart and brain. They reduce the risk of diseases like Alzheimer's by supporting the brain cell structure and improving communication between cells.
- Flavonoids: Flavonoids—found in berries, dark chocolate, and tea—can improve memory and learning by enhancing brain cell function and increasing blood flow to the brain.
Cardiovascular Health
Due to modern diets and the increased health risks of junk food, heart diseases are a leading cause of death globally. Nutraceuticals keep the heart healthy and reduce the risk of heart-related issues. They often include:
- Omega-3 fatty acids: These fatty acids reduce the fat in your blood (also known as triglycerides) and blood pressure, hence decreasing the risk of irregular heartbeats. They are mainly found in walnuts, flaxseeds and fish oil.
- Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10): It is an antioxidant and helps produce energy in cells, which increases the heart's efficiency, especially in people with heart issues.
- Plant sterols and stanols: These compounds lower cholesterol by blocking its absorption in the intestine. They are added to foods like margarine and orange juice.
- Fibre: Soluble fibre—found in oats, beans, and fruits—can lower cholesterol and improve heart health by reducing cholesterol absorption into the bloodstream.
Digestive Health
A healthy digestive system is essential for an individual's overall health. Nutraceuticals can improve digestion and enhance gut health. Some nutraceuticals which are suitable for the human digestive system are:
- Probiotics: These are live bacteria found in yoghurt and supplements. They help maintain a healthy amount of gut bacteria, which helps avoid conditions like irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease.
Source: Freepik
- Prebiotics: Prebiotics are nondigestible fibres that feed probiotics and are found in food items like onions and bananas.
- Digestive enzymes: Enzymes like amylase, lipase, and protease help in nutrient absorption and keep digestive discomfort at bay by breaking down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
Overall Wellness
Nutraceuticals provide all essential nutrients missing from the regular diet and promote the overall well-being of an individual. Nutraceuticals that improve overall wellness include the following:
- Antioxidants: Besides specific benefits for the brain and heart, antioxidants help reduce overall body stress and lower the risk of chronic diseases.
- Adaptogens: Herbs like ashwagandha, ginseng, and rhodiola help the body manage stress, reduce fatigue, and improve mental clarity.
- Collagen: This protein is essential for skin, hair, and nails and supports skin elasticity and joint health. Currently, collagen supplements are top-rated since they promise younger-looking skin.
What’s this Current Trend we’re seeing?
There are two reasons we’re seeing a lot more nutraceuticals today. The first is information. A decade ago, there wasn’t enough information to support their advantages and disadvantages. Over the years, a lot more information has been obtained, which makes it easier to understand and use them.
The second reason is personalization. If you’ve read our recent articles, you know already that the pharmaceutical industry is at the crux of a shift: personalized medicine is making huge headways. And, this personalization has also expanded to nutraceuticals.
Due to recent advancements in genomics, microbiome science, digital healthcare tools, and consumers’ demands, personalized nutraceuticals are cropping up. Here are a few key trends:
- DNA-based nutraceutical recommendations: Companies are offering nutraceutical products catered to your DNA. You simply complete and DNA test kit and send it in. Then, they analyze the genes related to metabolism, nutrient absorption, and deficient predispositions and develop personalized supplements. Some players in this field include DNAfit and Nutrigenomix.
- Microbiome-targeting formulations: These formulations help improve your digestive health, immunity, and mood. In brief, your gut biome is sampled and the best supplements to improve your gut ecosystem are recommended or produced. Some players in this field include Viome and DayTwo.
- AI-driven personalization: AI and ML algorithms are also used to assess user information like diet, biomarker reports, healthcare reports, etc., and the supplement dosage and ingredients are dynamically adjusted. Some players in this field include Baze and Care/of.
What do regulatory agencies say about this trend?
Different regulatory agencies have different outlooks on nutraceuticals. Here’s a brief overview:
- The US FDA considers nutraceuticals as dietary supplements. Hence, they don’t need FDA approval before marketing. Manufacturers can make function claims, but should also include a disclaimer stating that the FDA has not evaluated the product. However, the FDA does enforce post-market surveillance and action against misleading claims.
- The European Food Safety Authority regulates nutraceuticals under the Food Supplements Directive. They’re considered food products, not medication. All health claims are evaluated before approval. Pre-market, health claims need to be proven for product approval.
- The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India categorises them into several different categories. These products need pre-market approval and registration. Furthermore, labels cannot make disease treatment and prevention claims. Furthermore, licensing and compliance are frequently validated.
- Health Canada regulates these products as natural health products and requires pre-market approval. Manufacturers need to submit evidence of safety, quality, and efficacy. The products are under strong regulatory oversight and inspections.
- The Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan considers these products under two categories: Food for Specific Health Users (FOSHU) and foods with function claims (FFC). FOSHU products require approval, and FFC products don’t.
Conclusion
So, where does this leave me? Am I going to take supplements? Right now, probably not. I believe (and so does my doctor) that I’m getting sufficient vitamins and minerals from my daily diet. So, I can continue on this path and perhaps revisit the decision again down the line.
However, what’s concerning to me is that many people seem to be taking nutraceuticals only because someone they know is taking them. In reality, nutraceuticals should be consumed based on your lifestyle, diet and body needs. Regulatory agencies are still establishing guidelines for these products. So, instead of jumping on trends, understand what your body needs and do that!
FAQs
1. What are the examples of nutraceuticals?
Nutraceuticals include three product categories: functional foods, dietary supplements, and medical foods.
2. Can nutraceuticals replace prescription medications?
No, nutraceuticals can’t replace prescribed medications. They can be used in conjunction with medicines to ensure good health.




