by Mrudula Kulkarni
7 minutes
Quality Control in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Here, we delve into the significance of quality control in pharmaceutical manufacturing and its far-reaching implications for healthcare and society.

Every pill you take endures a journey of precision, perseverance, and purpose—so you don’t have to endure pain.
Behind that tiny tablet on your table lies an immense process, from intensive research and development to meticulously controlled pharmaceutical manufacturing process. Each step is marked by rigorous quality checks and adherence to strict protocols. It's not just about making medicine; it's about making it safe, effective, and reliable.
In an industry as competitive and tightly regulated as pharmaceuticals, quality control in pharmaceutical industry is not an option—it’s the very foundation. Because one oversight can mean the difference between healing and harm, every batch undergoes highly accurate, uncompromising scrutiny. When it comes to your health, quality is everything.
In this blog, we will discover the significance of quality control in the pharmaceutical industry, the steps of quality control in the pharmaceutical industry, the challenges, and the future of quality control. Let's dive in.
Function of Quality Control in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Patient Safety: Quality control in the pharma industry ensures medications are free from contamination and impurities, which helps protect patients from adverse effects.
Product Efficacy: Quality control ensures that drugs provide optimal therapeutic benefits by verifying potency and performance through in-process testing like PAT, as well as through assays and stability studies.
Regulatory Compliance: Adherence to GMP and standards set by regulatory bodies like the FDA and EMA ensures legal compliance and maintains high manufacturing standards.
Prevent Recall & Litigation: Timely identification of quality issues minimises the risk of expensive recall and legal actions and protects the brand image.
Continuous Improvement & Innovation: Quality control stimulates processing optimisation, waste minimisation and innovation in manufacturing and formulation.
Strong quality assurance for pharmaceuticals systems support these goals, ensuring every drug batch consistently meets safety and compliance standards.
Steps of Quality Control in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Quality control (QC) plays a critical role in pharma manufacturing by ensuring that every product is safe, effective, and compliant with regulations. From the raw materials up until the final product, here’s how the industry maintains the quality in check:
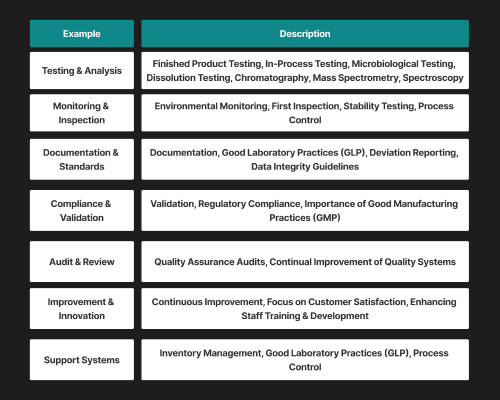
1. Raw Material Testing
All primary raw materials APIs, excipients and packaging, and others are tested for identity, purity and safety with sophisticated instruments like chromatography, spectroscopy, etc. This step prevents any contaminants from entering production.
2. In-Process Monitoring
While manufacturing, QC teams monitor essential elements such as temperature, pressure, pH, and mixing time. Real-time monitoring enables the detection of deviations at an early stage, making the process smooth and preserving its integrity.
3. Finished Product Testing
Before any medicine reaches patients, it undergoes rigorous testing like assays, dissolution tests, stability checks, leak tests and more. This confirms the product’s purity and shelf life.
4. Environmental Monitoring
Clean environments are non-negotiable when it comes to pharmaceuticals. QC teams constantly check for air quality, humidity, and microbial contamination has HVAC systems installed in production areas where HVAC systems are installed to prevent product from spoiling and stay GMP-compliant.
5. Quality Assurance Audits
Regular GMP audits of processes, training, equipment, and documentation help ensure full compliance. These audits are key to identifying gaps and maintaining high standards.
The quality control department in pharmaceutical industry oversees these steps, ensuring documentation, testing, and compliance are consistent across every stage of manufacturing.
Best Methods of Quality Control in the Pharmaceutical Industry
Challenges in Pharmaceutical Quality Control: Future Directions and Innovations
In the intricate realm of pharmaceutical manufacturing, ensuring product quality is paramount to safeguarding patient safety and maintaining industry integrity. However, the landscape of quality control in the pharmaceutical industry has challenges.
From evolving regulatory requirements to technological advancements, manufacturers face many obstacles in their quest for excellence. Discover how pharma quality control technologies are evolving to meet these demands.
Here, we explore the critical challenges faced by the pharmaceutical industry in quality control and examine future directions and innovations poised to address these challenges.
Modern approaches like AI and digital twins are enabling qc in pharmaceutical industry to move from reactive to predictive models, reducing recalls and ensuring patient safety.
Challenges in Quality Control
Keeping Up with Changing Regulations
Pharma companies must constantly adapt to evolving global regulatory standards, especially around data integrity, validation, and compliance. Staying audit-ready is a never-ending challenge.
Managing Complex Global Supply Chains
With raw materials and production spread worldwide, ensuring quality across every link from sourcing to shipping gets tougher.
Handling Big Data Effectively
Quality control teams deal with massive amounts of data from labs, manufacturing lines, and audits. Data integration to guide smart decisions isn’t easy when multiple manufacturing steps are involved.
Adopting New Technologies
AI, automation, and analytics are transforming pharma, but integrating digital tools transforming quality assurance without compromising compliance or data integrity takes careful planning and expertise.
Ensuring Quality with Outsourced Manufacturing
Outsourcing to global CMOs can boost efficiency, but it also means managing quality standards across diverse teams, cultures, and geographies.
Best Practices In Quality Control for 2025
Real-Time Monitoring and Process Control
Real-time monitoring and process control technologies can revolutionise quality control by enabling continuous monitoring of manufacturing processes and immediate corrective actions in response to deviations. This includes using process analytical technology (PAT), sensors, and automation systems to ensure real-time product consistency and quality.
What is PAT?
Process Analytical Technology (PAT) is a system that helps monitor and control pharmaceutical manufacturing in real time. It ensures product quality by tracking Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) during production, instead of only testing at the end.
The PAT analyses raw materials and products during the process and uses data analysis to predict and control quality. The technology also helps link Critical Process Parameters (CPPs) to product quality, enabling real-time adjustments to keep the process on track.
The Key Benefits include better product quality and consistency, resulting in less waste of energy and rework. Aid in faster production, reduced cycle time, real-time quality checks, and faster product release. The PAT supports continuous manufacturing instead of traditional batch processes.
Data Analytics and Artificial Intelligence
Leveraging data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) holds immense potential for enhancing quality control in the pharmaceutical industry. AI-driven algorithms can analyse vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict potential quality issues, enabling proactive risk mitigation and optimisation of manufacturing processes.
Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology appears to have a promising solution to increase pharmaceutical supply chain transparency, traceability, and security. Through blockchain-based solutions, manufacturers can monitor and validate the authenticity of raw materials, components, and finished products and guarantee quality and compliance in the supply chain.
Regulatory Harmonisation and Collaboration
The future of quality control in the pharmaceutical industry depends on regulatory harmonisation and collaboration between industry stakeholders and regulatory agencies.
Streamlining regulatory requirements, encouraging collaboration, and including standards such as the International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) can facilitate innovation and ensure consistent quality standards worldwide.
Leveraging Automation and Technology
Automation and digital technology drive modern pharmaceutical manufacturing. Adopting these technologies improves efficiency and especially the accuracy in quality control. Automation technologies empower manufacturers to stay ahead of quality issues rather than responding to them after the fact.
Automated Inspection Systems: Utilise machine vision and other automated inspection systems to detect defects more precisely.
Robotics in Production: Robotic systems bring consistency and reliability, reducing the error rate associated with manual labour.
Internet of Things (IoT): Connect machines, sensors, and quality control systems over IoT networks to enable real-time monitoring and data collection.
Conclusion
The foundation of safe, efficient, and dependable pharmaceuticals is quality assurance. Given the rise in global demand and regulatory expectations, it is impossible to overestimate the importance of quality assurance and quality control in the pharmaceutical industry.
Every stage is crucial, from using exact quality control techniques for pharmaceuticals to testing raw materials for pharmaceutical GMP quality control. Thanks to innovations like PAT, AI, and blockchain, the future promises smarter, faster, and more dependable oversight.
Effective quality assurance for pharmaceuticals ensures patients receive reliable medicines while also safeguarding the reputation of manufacturers worldwide.
FAQ’s
1. What are the GMP requirements for quality control?
Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) require pharmaceutical companies to implement strict quality control systems that ensure drug identity, strength, quality, and purity. This includes documented testing of raw materials, in-process checks, environmental monitoring, finished product testing, and proper equipment calibration. GMP also mandates accurate recordkeeping, staff training, and audit readiness to maintain compliance.
2. How does PAT support pharma quality?
Process Analytical Technology (PAT) enhances quality by enabling real-time monitoring of manufacturing processes. It helps track Critical Quality Attributes (CQAs) and Critical Process Parameters (CPPS), ensuring consistent product quality without relying solely on end-product testing. PAT allows quicker adjustments, reduces waste, and supports continuous manufacturing all key to modern, efficient pharma production.
3. Why is raw material testing critical in pharma manufacturing?
Raw material testing is essential to prevent contamination and ensure consistency from the beginning of the manufacturing process. It verifies the identity, purity, and safety of active ingredients and excipients, helping meet GMP quality control standards and safeguarding patient health.
4. What is the role of real-time monitoring in quality control?
Real-time monitoring enables pharmaceutical companies to track key process parameters as they happen, allowing immediate detection and correction of deviations. This improves product consistency, reduces waste, and supports faster decision-making and product release, especially when integrated with technologies like PAT.




