by Snigdha Joshi
8 minutes
The Real Story Behind Every Vaccine Shot
Explore the history, significance, and reality of vaccines, from early milestones to the future of immunization.
We're right in the middle of World Immunization Week. This week, Pharma Now is diving deep to help our audience understand the nuances of immunization. Of course, we can't discuss immunization without vaccines. So, in the first article in this series, let's know the milestones, significance, and reality of vaccines. We're here to provide you with in-depth information about vaccines.
Why Are They So Important?
Vaccines have been an instrumental part of every human fight against infectious diseases. From smallpox to polio, vaccines have saved millions of lives and eradicated many deadly diseases. They're not just protectors; they're preventers.
How's the journey been?
The journey's been loooong!
The concept of vaccination dates back to the late 18th century. In 1796, Edward Jenner introduced the first vaccine (for smallpox) and started a new branch of medicine—immunology!
Over the years, many new vaccines have been developed for diseases of all severity, from diphtheria to influenza. Notably, the polio vaccine, introduced in the 1950s, played a crucial role. It reduced the global polio incidence by 99%!
Since then, vaccine technology has rapidly evolved, and many important vaccines have been developed. You've probably heard of the latest breakthrough: mRNA vaccines for COVID-19, which are a completely different class of vaccines, showcasing their importance in the world.
Even after 3 centuries, are vaccines still relevant?
Yes, of course!
In fact, the COVID-19 pandemic underscored the benefits of a vaccine in managing a global health crisis. mRNA-based COVID-19 vaccines like those from Pfizer and Moderna and vector-based COVID-19 vaccines like that from AstraZeneca demonstrated modern science's potential to quickly and effectively manage emerging infectious diseases. Furthermore, they can also be used for treating chronic diseases, like HPV vaccines for cervical cancer.
As the WHO has repeatedly highlighted, vaccines are essential in safeguarding public health and preventing future pandemics.
We'll anticipate your next question: So, if they're relevant even after 3 centuries, how do they work?
How Does a Vaccine Work in Our Body?
Its job is quite simple to understand but difficult to achieve:
Vaccines train our immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens. When you're vaccinated, your immune system can produce memory cells, which recognize the pathogen, and produce antibodies, which fight the pathogen.
So, via vaccine immunization, you're making your body into a well-trained army.
Remember: A vaccine is different from a medicine. Vaccines train your body to fight diseases and prevent their occurrence, whereas medicines help your body treat an illness after it's happened.
How does a vaccine train our body?
First, when you get a vaccine, your body is introduced to a harmless part of the pathogen, which triggers your immune system to mount a defense.
Second, the immune system produces antibodies, which are proteins that target specific pathogens. The antibodies neutralize the pathogen. The immune system also creates memory cells, which remember how to fight this specific pathogen.
Finally, the immune system goes to work. It produces the necessary antibodies and memory cells for all pathogens and keeps them in the bloodstream, preventing the body from getting attacked by the same pathogen.
As we said, the job's simple, but only experts can do it. So, vaccines can't be used interchangeably, and many vaccines have been developed.
Which Type of Vaccine Are We Taking?
Different vaccines provide immunity in different ways. The major types of vaccines include:
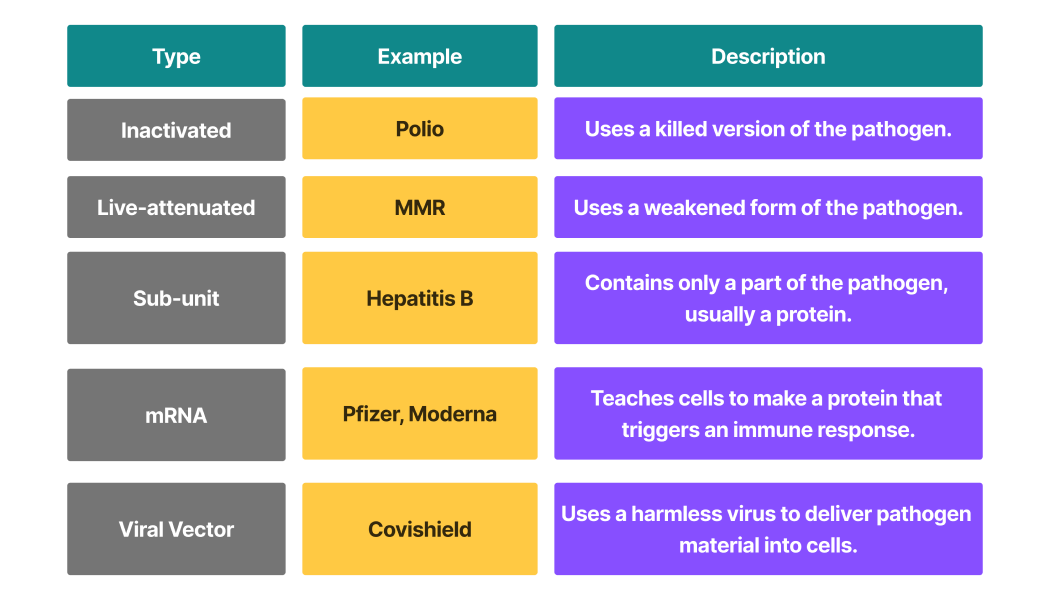
They are different because of how they're made and which part of the pathogen they use to trigger the immune system. You've probably taken many of these vaccine types in your life, or at least have encountered them before! How, you ask?
Who's Taking Vaccines, and When?
Vaccines are administered at various stages of life, from childhood to adulthood, and even in response to travel or specific diseases. Here's a brief classification:
- Childhood immunization: Newborns and infants receive their first doses within the first few months. Vaccines for various diseases like polio, DPT, and hepatitis B are given as part of a routine schedule around the world. For example, India's Universal Immunization program provides children with vaccines for tuberculosis, hepatitis B, and measles.
- Adult vaccines: Adults are also administered doses annually. For example, in certain parts of the world, adults get flu vaccine shots every year. Some adults also receive vaccines for upcoming diseases or for maintaining immunity, for example, COVID-19 vaccine booster doses.
- Travel vaccines: These vaccines are only given to travellers going to specific locations. For example, travellers to Angola are required to get vaccines for cholera, hepatitis A & B, malaria, measles, polio, rabies, typhoid, and yellow fever one month before their travel. Such vaccination requirements change from one location to another and over time.
There are, of course, many proven benefits of a vaccine; hence, all healthcare bodies and professionals always stay updated with vaccination requirements.
Still, there are many myths surrounding immunization.
Myths vs Reality: Vaccine Edition
😱 "Vaccines cause autism!"
No. In fact, many studies have proven that there's no link between the two, and vaccination is quite safe!
😌 "We should rely on natural immunity!"
Natural immunity is effective, but it often comes at the cost of sickness. Vaccines are a safer way to help our bodies build immunity!
🥴 "Vaccines overwhelm the immune system!"
Actually, our bodies can handle multiple vaccines at once.
👍 "Good hygiene can reduce disease rates!"
Research shows that vaccines, and not hygiene, are responsible for a sharp drop in disease and death rates.
🤷 "The disease has disappeared, so why should I take it?"
The disease may have disappeared from specific countries, but it is prevalent in many other countries. Without vaccination, outbreaks can still happen!
Many vaccinations often work on herd immunity.
What's Herd Immunity?
Herd immunity occurs when a sufficient percentage of the population is immune to a disease, either due to vaccination or prior infection. Hence, the spread of the disease is minimized because fewer people can be infected. This helps protect people who can't be vaccinated, for example, children and immunocompromised individuals.
So, by vaccinating yourself, you're not only protecting yourself, but also protecting others!
How Are We Getting Vaccines?
Vaccines need to be stored at specific temperatures to remain effective, even during transport. Hence, the industry uses "cold chain".
Is that easy?
No, not really. Over the years, the industry has perfected cold chain logistics in many countries. However, in remote regions and growing countries with challenging architectures, maintaining a cold chain is difficult.
Solution?
Solar-powered refrigerators and sensors are used to track whether the cold chain is broken.
What's on the Agenda?
Considering the importance and criticality of vaccination, many have developed vaccination-related agendas:
- WHO's Immunization Agenda 2030 has set the goal of vaccinating 70% of the global population by 2030.
- The GAVI Alliance is working with governments, private companies, and healthcare professionals to secure funding for vaccines for the world's poorest countries.
- India's Mission Indradhanush aims to increase immunization coverage for Indian children, particularly in remote and underserved areas.
- The Big Catch-Up is an initiative by WHO, UNICEF, and GAVI that aims to restore immunization coverage to pre-pandemic levels by reaching children who missed routine vaccines due to the pandemic.
- The 22nd Vaccination Week in the Americas is an annual campaign aiming to boost vaccination in the Americas.
Where Are We Heading?
The future of vaccines is very exciting; in fact, we can think of three new advancements on the horizon:
- AI and vaccine discovery: AI can speed up vaccine discovery by enabling the identification of potential candidates.
- Nasal, oral, and edible vaccines: Nasal, oral, and edible vaccines are being studied to make vaccination less invasive.
- Pan-virus vaccines: Researchers are trying to develop vaccines that can protect against multiple viruses!
What's Our Role?
Vaccines make huge contributions to public health. But, as we've mentioned before, the work isn't done yet! Here's how you can contribute:
- Stay Informed: Read articles to understand the importance of vaccines and their role in disease eradication.
- Get Vaccinated: Do your part by staying up to date on all vaccinations, which will protect you and others!
Spread Awareness: Doubt whether the "Fun Fact About Vaccines" is a Myth or Reality? A quick Google Search will give you the right answer! Don't forward messages blindly!




