by Vaibhavi M.
null minutes
AI In Clinical Trials: Recruitment, Site Selection & Patient Monitoring In the Pharmaceutical Industry
AI accelerates clinical trials with smarter recruitment, site selection, and real-time patient monitoring.

The pharmaceutical industry is undergoing a rapid digital transformation, and nowhere is this shift more visible than in clinical research. Artificial intelligence (AI), once considered an experimental add-on, has now become a core driver of efficiency, precision, and innovation across clinical development. From patient recruitment and protocol design to site selection and remote monitoring, AI is reshaping how trials are planned, executed, and analysed.
As the volume of biomedical data grows exponentially, driven by electronic health records (EHRs), digital biomarkers, genomics, real-world evidence (RWE), and wearable technologies, AI has emerged as the only scalable solution capable of converting this massive data landscape into actionable insights. The result is faster trials, better patient outcomes, and more predictable regulatory compliance.
This blog explores how AI is redefining three critical elements of modern clinical trials: patient recruitment, site selection, and patient monitoring, along with the challenges, opportunities, and future trajectory of this evolving ecosystem.
AI-Powered Patient Recruitment: Solving The Industry’s Biggest Bottleneck
Patient recruitment remains the single largest cause of trial delays. Estimates suggest that nearly 80% of clinical trials fail to meet enrollment timelines, and over 30% of Phase III trials are terminated primarily due to insufficient recruitment. The traditional recruitment model, physician referrals, hospital databases, and manual outreach, is slow, expensive, and often ineffective.
AI is transforming this process through:
1. Intelligent Patient Identification
AI algorithms analyse structured and unstructured data from EHRs, medical images, lab data, physician notes, and patient histories to match eligible participants with protocol criteria. Natural language processing (NLP) helps interpret complex case notes, making it easier to identify nuanced inclusion and exclusion criteria such as mutation profiles, comorbidities, and prior treatment responses. Instead of spending weeks manually screening records, researchers can instantly sort thousands of patient profiles in minutes.
This allows recruitment teams to:
- Detect eligible candidates faster
- Reduce screen failure rates
- Expand recruitment beyond single sites to nationwide or global databases
2. Predictive Recruitment Forecasting
Beyond identification, AI predicts how many patients are available, how likely they are to consent, and how recruitment numbers change over time. These predictive models help pharmaceutical companies optimise recruitment timelines and allocate recruitment budgets based on actual data instead of assumptions.
3. Personalised Patient Engagement
AI chatbots, multilingual conversational AI, and automated follow-up systems improve engagement by answering patient queries, sending reminders, and offering personalised support. This reduces dropout rates and increases trust, an essential factor in long-term clinical studies.
AI in Site Selection: Eliminating Guesswork And Improving Trial Performance
Traditionally, site selection relied on historic performance, investigator experience, and manual feasibility assessments. AI introduces a data-driven, unbiased, and evidence-based approach. Site selection is another major challenge in clinical development. Poor site selection leads to:
- Slow enrollment
- High costs
- Inconsistent data quality
- Risk of trial failure
1. Advanced Feasibility Modelling
AI integrates multi-source datasets, including historical trial data, investigator performance metrics, regional disease prevalence, demographic datasets, real-world healthcare utilisation data, and regulatory performance benchmarks, to generate a holistic feasibility score for each potential site. This helps pharma sponsors identify sites that will deliver the highest enrollment efficiency and strongest data integrity.
These models can evaluate:
- Expected recruitment potential
- Site workload and staff availability
- Prior protocol compliance
- Infrastructure adequacy
- Patient-to-site distance
- Laboratory turnaround time
2. Investigator Performance Prediction
Machine learning models track investigator-level performance over time and predict future productivity. Using these insights, sponsors can make informed decisions about reactivating past sites or onboarding new ones.
This includes:
- Time to first patient in (FPI)
- Average recruitment per month
- Data query resolution time
- Protocol deviation history
3. Geographic and Demographic Optimisation
Analysing regional disease burden, socioeconomic factors, and age distributions helps AI recommend optimal geographic locations for trials, particularly valuable for oncology, rare diseases, and population-specific drug development.
This is especially critical for increasing diversity and meeting FDA guidelines on inclusive research. AI ensures that trial populations better reflect real-world patients by identifying underserved regions or populations that fit the study’s demographic needs.
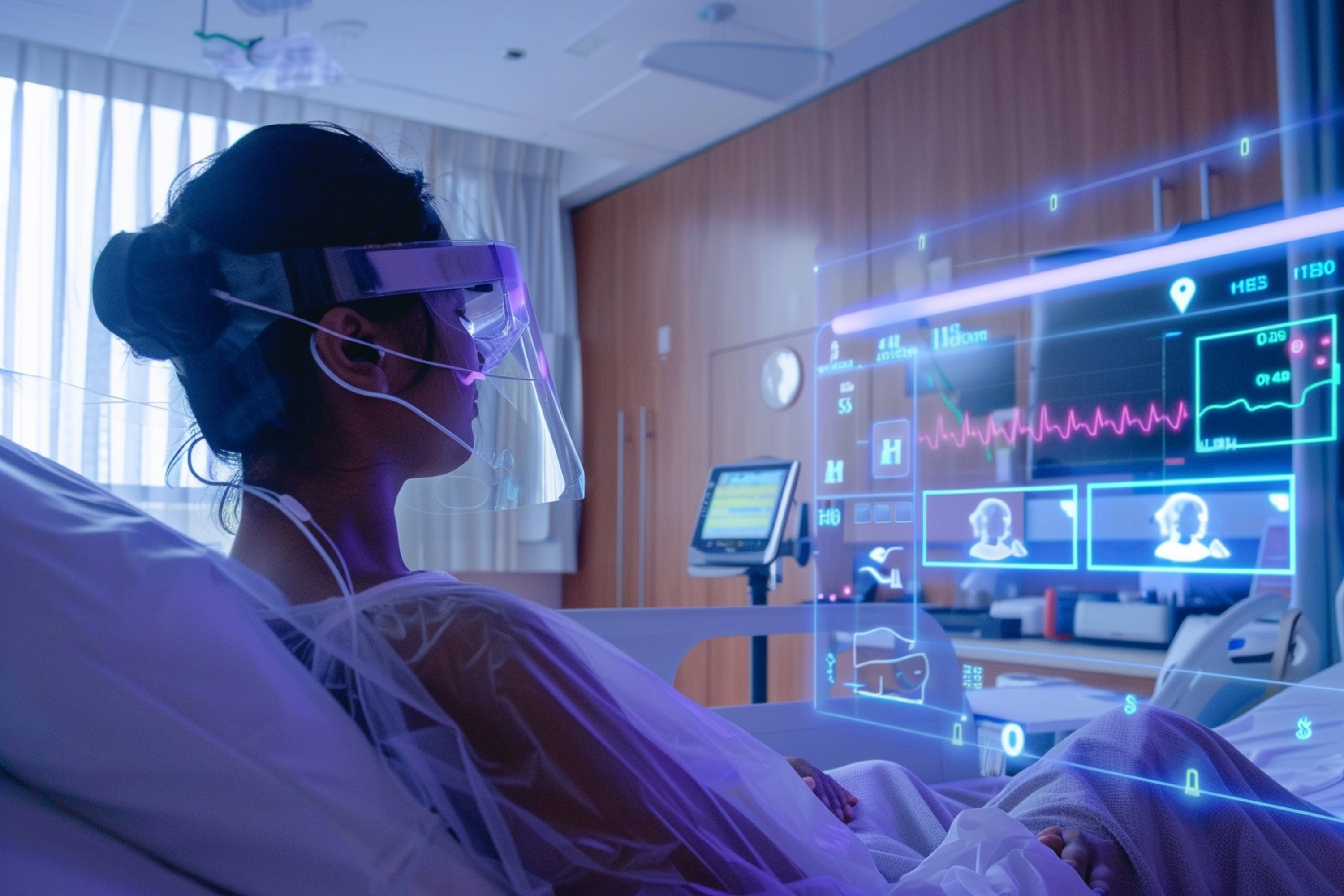
AI-Driven Patient Monitoring: Real-Time, Continuous, and Accurate
Once a trial begins, patient monitoring becomes the backbone of data accuracy, compliance, and safety. Traditional monitoring relies on periodic site visits, paper diaries, and self-reported outcomes, all of which can introduce variability and data gaps.
AI enables a shift toward continuous, remote, and predictive patient monitoring, improving both protocol adherence and patient safety.
1. Digital Biomarkers and Wearable Integration
Wearables, biosensors, and connected medical devices generate real-time physiological data such as:
- Heart rate variability
- Blood oxygen levels
- Physical activity
- Sleep patterns
- Glucose fluctuations
- Medication adherence
AI models analyse this data to detect patterns and deviations early. For chronic diseases, oncology, neurology, and metabolic disorders, these digital biomarkers offer unprecedented visibility into patient health trends.
2. Early Adverse Event Detection
Machine learning algorithms can identify subtle physiologic anomalies that may precede adverse events. For example, AI-enabled monitoring systems can detect cardiac toxicity early in oncology patients or predict hypoglycemic episodes in diabetes studies.
By flagging risks earlier than traditional methods, AI enables:
- Proactive clinical intervention
- Dose adjustments
- Reduced hospitalization
- Improved patient safety outcomes
3. Automating Data Cleaning and Validation
One of the biggest challenges in patient monitoring is data quality. This reduces the burden on clinical research associates (CRAs), speeds up data processing, and ensures higher data reliability.
AI can automatically:
- Identify missing or inconsistent data
- Detect outliers
- Validate data formats
- Flag non-compliance
- Standardise multi-source datasets
4. Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM) and Virtual Trials
The rise of decentralised clinical trials (DCTs) accelerated the adoption of AI tools for remote patient oversight. Combined with telemedicine, AI supports a patient-centric approach, making participation more accessible and reducing the burden of travel, especially beneficial for elderly or mobility-challenged patients.
AI simplifies virtually every component of DCTs:
- Digital consent and onboarding
- Remote assessments
- Video symptom monitoring
- Automated adherence tracking
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its advantages, AI in clinical trials requires careful consideration of regulatory, ethical, and operational challenges.
Data Privacy & Security:
AI depends heavily on sensitive patient data. Ensuring HIPAA, GDPR, and local regulatory compliance is essential to maintaining patient trust.
Algorithmic Bias:
If AI systems are trained on biased datasets, they can unintentionally exclude certain populations from screening or recruitment. Sponsors must ensure model transparency and diverse training datasets.
Regulatory Acceptance:
Although regulatory authorities globally are embracing AI, companies still need to document algorithm performance, validation, data lineage, and model explainability.
Integration Challenges:
AI platforms must integrate seamlessly with legacy systems such as EHRs, CTMS, EDC, and LIMS to avoid workflow disruption.
Human Oversight:
AI augments, not replaces, clinical decision-making. Ensuring appropriate human-in-the-loop processes is essential for maintaining accuracy and ethics.
The Future of AI in Clinical Trials
The next decade will see AI evolve from supportive technology to a central operational driver. Emerging developments include:
- Multi-omics integration for personalised trial matching
- Synthetic control arms reducing placebo burden
- Autonomous monitoring using smart devices
- Digital twin simulations predicting trial outcomes
- AI-powered adaptive trial designs
As trials become more decentralised and data-rich, AI will increasingly determine trial planning, recruitment, monitoring, and analysis, reducing timelines and improving success rates.
The pharmaceutical industry is shifting from reactive decisions to predictive, precision-driven, and patient-centric clinical development, and AI is the engine powering this transformation.
FAQs
1. How is AI used in clinical trial patient recruitment?
AI screens EHRs, lab data, and health records to identify eligible participants faster and reduce screen failures.
2. What role does AI play in clinical trial site selection?
AI analyzes historical performance, patient availability, and regional disease trends to choose the most effective trial sites.
3. How does AI improve patient monitoring during trials?
AI uses wearables, biosensors, and real-time analytics to detect anomalies early and ensure continuous monitoring.
4. Are AI-driven clinical trials faster than traditional models?
Yes, AI reduces recruitment delays, automates monitoring, improves data quality, and shortens study timelines.
5. Is AI accepted by global regulatory authorities in clinical trials?
Regulators increasingly support AI, provided companies demonstrate model validation, transparency, and compliance.