by Ravindra Warang
7 minutes
Pharmaceutical Supply Chain Management: Fundamentals and Best Practices
Explore the key components, best practices, and common challenges in pharmaceutical supply chain management.

Last week, a colleague who was taking medication read the manufacturer's address on the back of the strip and asked me, “How did they manage to ship this all the way from Germany in five days? The manufacturing date is only five days ago!” It was a perfect opportunity for me to explain the complex web of supply chain management, which I did.
But that conversation made me realize that most people don’t know the networking, planning, management, and difficulties that the pharmaceutical companies have to overcome to ship their products from one place to another.
So, this article unveils the fundamentals of supply chain management and some of the common strategies companies use to make their supply chains resilient. To better understand the direction the industry is heading, explore key pharmaceutical supply chain trends that shaped 2024 and continue to influence decision-making today.
Fundamentals of Supply Chain Management
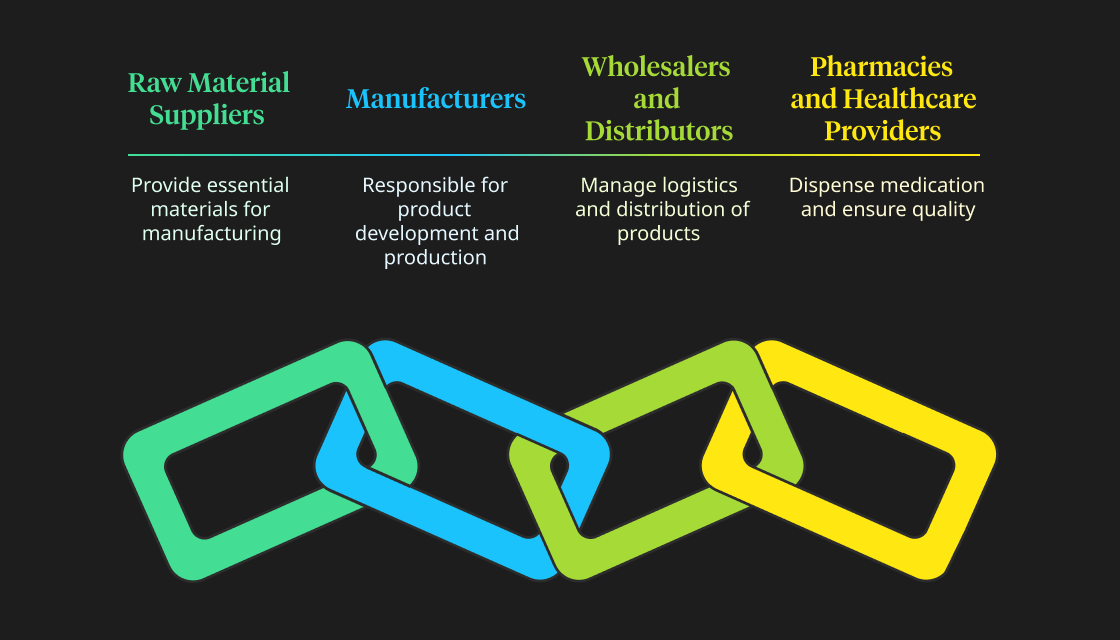
The fundamental components of pharmaceutical supply chain management are as follows:
Raw Material Suppliers
Raw material suppliers are the first and foremost component because, without raw materials, manufacturing is impossible. Raw material suppliers determine the amount of goods that can be manufactured. Consequently, companies must maintain a docket of suppliers and excellent relations with each other.
Manufacturers
Manufacturers include the R&D and production departments responsible for ideating and manufacturing the product. They hold an essential role in pharmaceutical supply chains because there would be no new products without them.
Wholesalers and Distributors
Wholesalers and distributors connect pharmaceutical manufacturers to patients or healthcare providers. They act as middlemen and often manage the logistics and distribution of products within a specific region. They usually have extensive freight and logistics networks, allowing them to distribute products promptly.
Pharmacies and Healthcare Providers
These are the points of sale for pharmaceutical companies because these are the points at which the patient purchases the product. Pharmacies dispense the medication to patients, and healthcare providers prescribe it, resulting in sales.
Both of these also perform quality checks to determine the efficacy of products, and upon this, the future prescriptions of a product are decided.
All companies must manage all stakeholders appropriately to ensure smooth pharmaceutical supply chain management, and the true test of their management skills comes when the world faces an endemic, epidemic, or pandemic. The recent COVID-19 pandemic revealed the importance of resilient pharma supply chains.
The Importance of Supply Chains in the Post-Pandemic World
Here’s why supply chains (and their resilience) have become very critical in the post-pandemic world:
- Disruption lessons: The recent pandemic exposed the vulnerabilities of global supply chains. There were shortages of essential medical products and long lead times. These disruptions explained, very clearly, why building supply chains was important.
- Global connections: Today, disruptions in one region can have global effects. For example, a war in Europe can raise fuel prices in Asia and Australia. In the pre-pandemic world, these effects were not given much importance. However, since the pandemic, companies have realized that they must prepare their supply chains for future shocks.
- Consumer expectations: Since the pandemic, consumer expectations have shifted. Today, patients want more transparency, faster deliveries, and real-time tracking. Consequently, pharma companies have had to adapt to keep up with these demands.
These have fueled pharma companies to invest in building resilient supply chains. While each company follows a different route to achieve these goals, most employ a few common strategies.
Top 7 Strategies for Resilience in Supply Chains
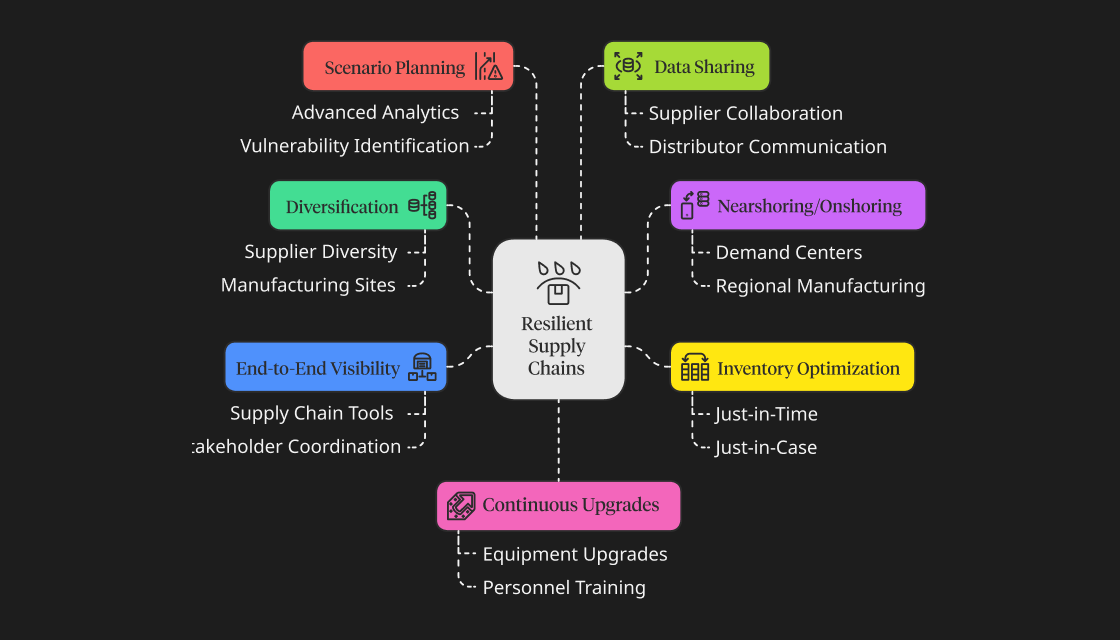
Here are the top few strategies used by companies to build resilient supply chains:
- Diversification is key: To build resilient supply chains, pharma companies diversify their suppliers and manufacturing sites. They prevent overdependence on a single source or region and adopt a multi-sourcing method to ensure they always have alternatives available during disruptions.
- Use nearshoring and onshoring: While companies often offshore manufacturing practices to reduce costs, this can create challenges in supply chain management during disruptions. Hence, companies can shift critical manufacturing practices closer to demand centers or in the same region/country.
- Inventory optimization: Another strategy that most companies use is balancing just-in-time and just-in-case inventories. They maintain buffer inventories of critical materials to hedge against disruptions.
- End-to-end visibility: The supply chain involves many stakeholders, all of whom have some inventory. Hence, companies use advanced supply chain tools to ensure the product is moving appropriately throughout the supply chain.
- Scenario planning: Companies often undertake scenario planning using advanced analytics tools to identify supply chain vulnerabilities and predict disruptions. This allows them to develop solutions to solve the problem before it occurs.
- Data sharing: Another strategy to build resilient supply chains is collaborative relations. When companies share data across the supply chain–suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, and sellers–they can better predict disruptions and better solve problems.
- Upgrade. Upgrade. Upgrade: Finally, companies always keep an eye out for ways to upgrade themselves. This not only includes upgrading equipment and tools but also technologies, personnel and knowledge.
While following these strategies, remember to follow these best practices as well.
Best Practices in Supply Chain Management
Here are some techniques for effective pharmaceutical supply chain management:
Embrace Supply Chain Management Technologies
Digital transformation 4.0 in the pharmaceutical industry revolves around supply chain management technologies. Consequently, pharmaceutical companies should also integrate upcoming technologies such as intelligent inventory management systems, predictive analytics, real-time tracking, and risk management software to mitigate potential supply chain failures. To get a deeper look into how this plays out, explore how pharma supply chain visibility tools are tackling traceability and communication gaps.
Understand Regulatory Requirements
The pharmaceutical industry is among the most regulated industries in the world. Therefore, when setting up and managing supply chains, it is necessary to ensure they comply with the regulatory requirements of local and international regulatory bodies. Non-compliance can have legal and financial consequences such as product loss, warning letters, fines, and litigation.
Optimise Logistics and Distribution
Pharmaceutical companies should invest time and money in making the logistics and distribution of their products more efficient, for example, establishing well-travelled distribution routes, consolidating shipments, and ensuring cold-chain integrity. By optimising logistics and distribution, companies may face fewer supply chain inefficiencies.
Foster Relations
Distributors, suppliers, wholesalers, regulatory authorities, and healthcare providers are the company’s backbone because they are responsible for the sale. Therefore, pharmaceutical companies need to foster relations among all key stakeholders. This ensures all appropriate contracts are renewed on time, closing all communication gaps and maintaining mutual trust.
However, despite following the best practices in the supply chain, pharmaceutical companies face several challenges.

Challenges Facing Supply Chain Management in Pharmaceuticals
Regulatory Compliance
One of the biggest challenges in pharmaceutical supply chain management is regulatory compliance. The transportation and storage of medication and pharmaceutical products must comply with strict guidelines implemented by the FDA and EMA.
This poses challenges when transporting products across large distances, such as from Asia to Europe. Furthermore, because regulatory guidelines are constantly changing, manufacturers have to update their procedures to stay updated and compliant continually.
Demand and Supply Fluctuations
The pharmaceutical industry faces product demand for various reasons (e.g., expiration, transportation delays, overstocking, etc.). Consequently, companies must adapt supply chain management to predict the market appropriately. Overproduction can lead to product wastage, which means financial loss, whereas underproduction can create demand issues.
Manufacturers need to accumulate appropriate product qualities, which is a thin balance. They use sophisticated technologies to predict demand, but these are not foolproof, and companies must account for fluctuations. Effective inventory management in pharma is essential to reduce losses and maintain stable product availability amid demand volatility.
Counterfeit Medication
Between 9% to 41% of medicines sold in low- and middle-income countries are counterfeit. Consequently, companies often have to face legal issues. However, companies must integrate sophisticated supply chain management technologies to combat counterfeits and track all consignments at every step. The integration and maintenance of these technologies are expensive and time-consuming, but necessary.
Supply Chain Inefficiencies
Pharmaceutical companies need to develop solutions for supply chain inefficiencies. Delays or disruptions in transportation can result in medication shortages or stockouts. These can happen due to poor supply chain management, poor infrastructure, inaccurate timelines, poor coordination, etc. Consequently, companies need to use data and predictive analysis for pharmaceutical supply chain management.
An Unexpected Challenge: Sustainability in Pharma Logistics
The pharmaceutical industry is gearing up for a new change, all brought on by the increased pressure to become sustainable. As the public becomes more aware of the pollution caused directly and indirectly by the pharmaceutical industry, they’re putting increasing pressure on the industry to adapt sustainable practices.
In fact, global regulatory agencies have also bowed to these demands, and many agencies have increased sustainability requirements for pharma companies. For example, the EU Plastics Strategy, the Industrial Emission Directive, and the Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation are some regulatory initiatives.
For pharma companies to comply with these guidelines, they need to make significant changes to their current supply chains. Here are some steps companies may have to take:
- Fleet upgrade: Pharmaceutical products are often transported via fuel-based vehicles like lorries, trucks, ships, etc. For sustainability, companies may have to shift from fuel-based vehicles to solar or electric vehicles.
- Packaging changes: Product packaging is a major concern in pharmaceuticals because plastic is commonly used. Hence, companies will have to shift to more eco-friendly and biodegradable products.
- Emission reduction: Pharmaceutical manufacturing results in a lot of emissions and wastewater generation, both of which considerably compromise the ecosystem. Hence, companies will have to adopt new technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and better treat wastewater before discharge.
Conclusion
Pharmaceutical supply chain management is a crucial task involving many stakeholders and variables. With this article, we aim to help you understand some of the fundamentals, strategies, and best practices of supply chain management. Today, supply chains face many challenges, and the solution to these challenges is planning.
Integration of supply chain management technologies allows companies to track all consignments. The data from these supply chain management technologies can be used to predict future demand and manufacture and stock products accordingly.
To see how leading companies are applying these insights at scale, check out this guide to optimizing pharma supply chains using automation and advanced analytics. Ultimately, pharmaceutical supply chain management depends heavily on data, and it is ill-advised to make decisions not backed by data.
FAQs
1. Who is involved in the pharmaceutical supply chain?
Raw material manufacturers/sellers, distributors, wholesalers, pharmacies, and healthcare providers are involved in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
2. What strategies are followed by pharmaceutical supply chain management?
All companies follow no specific strategy. However, most companies use supply chain management technologies to develop unique strategies to overcome general supply chain problems.
3. Can technology be used for pharmaceutical supply chain management?
Supply chain management technologies such as AI and data-driven analytics can predict demand and adjust supply accordingly. They can also determine potential failures or risks in the supply chains.
4. What are the key components of pharmaceutical supply chain management?
The pharmaceutical supply chain management includes raw material suppliers, manufacturers involved in research and development and production, wholesalers and distributors handling logistics and distribution, and pharmacies or healthcare providers responsible for sales and quality checks.
5. Why is resilience important in pharmaceutical supply chains, especially post-COVID-19?
Resilience in pharmaceutical supply chains ensures continuous availability of medicines despite disruptions. The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted vulnerabilities leading to supply chain disruptions, prompting investments in resilient strategies like diversification, nearshoring, inventory optimization, and enhanced visibility to meet global connections and rising consumer expectations.
6. What are the best practices for optimizing pharmaceutical supply chain logistics?
Best practices include establishing efficient distribution routes, consolidating shipments to reduce costs, ensuring cold-chain integrity for temperature-sensitive products, embracing advanced technologies such as intelligent inventory management systems and predictive analytics, complying with regulatory requirements, and fostering strong relationships with stakeholders like distributors and healthcare providers.
7. What common challenges does pharmaceutical supply chain management face?
Pharmaceutical supply chains encounter challenges such as stringent regulatory compliance, fluctuating demand and supply dynamics, risks of counterfeit medications—particularly prevalent at 9-41% in low- and middle-income countries—and inefficiencies within logistics and distribution processes.
8. How is sustainability being integrated into pharmaceutical supply chains?
Sustainability pressures from regulations like the EU Plastics Strategy, Industrial Emission Directive, and Ecodesign for Sustainable Products Regulation drive the pharmaceutical industry to adopt eco-friendly measures such as upgrading fleets to solar or electric vehicles, shifting to sustainable packaging solutions, and reducing emissions through innovative technologies.
9. How does data-driven management enhance pharmaceutical supply chains?
Data-driven pharmaceutical supply chain management leverages real-time data analytics for scenario planning, end-to-end visibility, demand forecasting, and continuous upgrading. This approach improves decision-making accuracy, enhances responsiveness to market changes, optimizes inventory levels, and strengthens overall supply chain resilience.




